The African economy is growing — fast. According to the IMF’s World Economic Outlook Report, 11 of the 25 fastest growing economies are countries are in Africa! There is a particular emphasis on the emergence of the eCommerce sector. McKinsey estimates that Africa’s iGDP (the Internet’s contribution to GDP) will reach $300 billion, 10% of Africa’s overall GDP, by 2025. However, eCommerce isn’t without its set of challenges.
Here are the top five eCommerce challenges in Africa, and how online merchants can overcome them:
1. Mistrust of online shopping
Many Africans are slow to trust online stores with their personal payment details. This stems from lack of knowledge about online payment systems and advanced security measures.
In order to overcome this mistrust, consumers should be educated as to how online payments work. In addition, merchants should use a PCI DSS certified payment service provider (PSP) that meets high security standards and keeps customer information safe. If customers understand how online fraud is prevented and the techniques that are used to prevent security breaches or fraud attempts, they are more likely to trust an eCommerce website with their payment information.
2. Fragmented markets
Africa has a diverse population with different cultures, politics, and economics. As a result, country-specific eCommerce companies have opened up. Across Africa, there is a duplication of resources which affects the economy negatively. Making cross border payments, dealing with tariffs and taxes, and meeting various country-specific legal requirements makes it difficult for countries to operate within the region, outside their own country.
To operate across countries and bridge fragmented markets, merchants should use a PSP such as Direct Pay Online.
Direct Pay Online makes it easy for merchants to serve customers in different countries, allowing for multicurrency cross-border payments and a range of payment options to suit every type of customer.
Another step that can be taken to overcome the challenge of fragmented markets is to introduce free trade zones and initiatives whereby tariffs and taxes are eliminated for cross-border transactions. This would greatly benefit the African economy.
3. People prefer to pay with cash
Africans are accustomed to using cash. It’s more familiar and tangible than digital payments, which are fairly new on the scene. However, CoD (cash-on-delivery) in eCommerce is more expensive and involves a high level of risk. A delivery driver is responsible for the company’s cash, and is more prone to becoming a victim of theft. CoD also makes it easier for customers to decline the delivery and refuse to pay, putting the cost of the delivery and return of the merchandise on the merchant, without any gain.
With digital payments, transactions are carried out before delivery, and drivers don’t need to carry any money around with them – completely eliminating the risks.
To encourage digital payments, merchants could create special promotions, offers or deals for customers choosing to carry out payments online. Merchants should also provide information about online payments on their websites and display trust icons and proof that their sites – and customer payment details – are secure.
4. Delivery logistics
In some ways, Africa’s transportation and delivery system is not equipped to deal with the booming eCommerce industry. Many African roads are not paved, and the terrain is often difficult for travel. This has created obstacles for eCommerce merchants seeking viable delivery options.
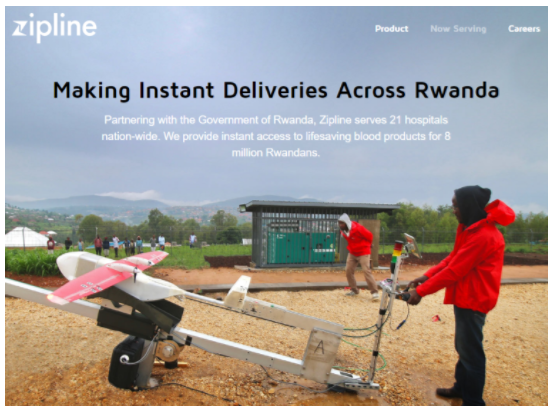
Two new developments that can help overcome delivery problems are drone delivery and crowdsourced delivery options. Recently, commercial drone deliveries were launched in Rwanda, by US startup Zipline. This has helped overcome Rwanda’s hilly terrain, which makes it difficult for deliveries to be carried out by cars or motorcycles.
These drones are currently being tasked with delivering blood to remote health centers just 30 minutes after receiving a request by text message. But in the future, it’s expected that drones will be used for more commercial applications – including eCommerce deliveries.
Crowdsourced delivery options are opening up, too. One example is MAX (Metro Africa Xpress), a Nigerian startup that provides delivery services using independent and crowdsourced drivers. If these options are applied across the continent, it could make eCommerce a lot easier, more efficient and more cost-effective.
5. Internet connectivity
Less than one-third of the African population has an Internet service that allows them to order goods online. As the Internet is expensive, online shopping has not been an option for everyone.
Infrastructure development is the key to providing Internet to more of the population. Fiber optic networks and other solutions are currently in development. These solutions provide infrastructure and reduce the expenses involved in connecting to the Internet.
The majority of urban Africans have some kind of device that can connect to the Internet. Even in rural areas, where infrastructure is inadequate, Africans can use their mobile phones to connect. If merchants invest in a mobile-optimized online store, and accept mobile payments, they can reach more customers.
In the upcoming years, we can expect increased implementation of innovative technologies, including drone deliveries, mobile payments, and fiber optic infrastructures. This, together with education about the safety and convenience of online payments, makes the future of African eCommerce extremely promising.