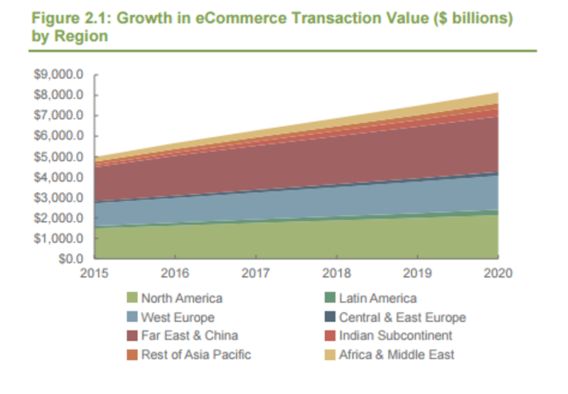
Retail ecommerce sales were valued at over $5 trillion in 2016, and projected to reach over $8 trillion in 2020, according to a 2016 Juniper Research study. With the rise in ecommerce, however, comes an increase in fraud attempts. Juniper found that in 2015, 1 out of every 67 transactions was a fraudulent attempt — up 7.1% from 1 out of every 72 transactions in 2014.
There are a variety of fraud and security threats to ecommerce websites, the most common of which are:
Unauthorized Data Access:
Hackers can breach non-secure sites and steal their databases of user information, such as payment data, and other sensitive information.
Malware:
eCommerce sites which are not sufficiently protected are vulnerable to malware threats such as viruses, worms or Trojans. Malware can infect website users, and even download software to their devices, without permission. This software can then perform a variety of functions, such as stealing, encrypting or deleting sensitive data, altering or hijacking computing functions and monitoring the user’s activity.
Phishing
Fraudsters set up a website which looks and feels like an existing site, and invite users to this imposter site. This fake site is a basis for obtaining users personal information, payment information, user names and passwords, as well as other private data. This usually restricted data can then be misused by these cyber criminals.
Denial of Services:
Hackers can cause server failure by sending huge volumes of automated requests to ecommerce sites. When the server attempts to reply to these requests, it cannot handle the volume, which leads to failure, slowing down the response rate or blocking new visitors.
Security best practices for ecommerce sites
To combat fraud threats like the ones described above, ecommerce operators must implement best practices and security measures to protect themselves and their users. Some examples of must-have security measures include:
1. PCI DSS compliance
Created jointly by the main credit card companies, The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a set of policies and procedures that optimize the security of payment via credit or debit card. These procedures include methods to protect credit card data, encryption, anti-malware software implementation and more, as well as ongoing monitoring and risk analysis.
One of the best ways to obtain the required level of monitoring and compliance is to work with a PSP (payment service provider) that already has PCI DSS certification and who can provide hosted payment pages that include leading security technologies.
2. HTTP over SSL (HTTPS)
Hypertext Transfer Protocol with Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), or HTTPS, uses a secure, encrypted protocol to transfer data online. Considered mandatory for PCI compliance, SSL certification encrypts and secures all sensitive information sent over the internet, protecting against eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks. The data is rendered unreadable to all, apart from the destination server, thereby ensuring a high level of data security. This protocol does not have to be integrated on all web pages, only on those with sensitive data.
HTTPS can be implemented by following these 5 steps:
Make sure your website has its own dedicated IP address
Buy a certificate from a reliable provider, like GoDaddy.
Have your web host activate your certificate
Ask your web host to also install the certificate
Update the URLs on your site to use HTTPS
3. Two factor authentication / tokenization
Two factor authentication requires the user to supply two means of identification, such as user name/password and a code that was received by SMS on the user’s mobile. By combining a password identification method with a limited time unique code, an extra layer of security is applied to ecommerce transactions. For example, leading websites, such as Gmail, often opt for this security measure to ensure their user’s privacy.
Tokenization, on the other hand, protects sensitive information, such as credit card data, by replacing them with random tokens, so that they cannot be read if intercepted or stolen. The data can only be deciphered by an authorized third party, such as the tokenization supplier or payment processor.
4. DoS and DDoS protection via firewall integration
As it is difficult for websites to purchase the required bandwidth to counter a DoS/DDoS attack, integration of firewalls can prevent these attacks. Effective firewalls for ecommerce sites include application gateways and proxy firewalls, which function as intermediary programs, ensuring communication only through authorized entities.
Implementation of this security measure can be done through a website hosting company (with packages that include firewalls) or through a third-party security technology provider.
Adopting online payments in Africa
With ecommerce becoming increasingly more popular, African ecommerce sites must accept online payments in order to grow, both domestically and internationally, and to successfully compete with global providers. Online payments open new markets to African companies and are more profitable than traditional sales. Plus, satisfied customers will happily return to a site they know and trust, further increasing revenues.
It is crucial that African merchants implement the above best practices in order to ensure secure transactions over their sites. The practices might seem daunting, making merchants consider putting off integration of digital payments on their sites, and ultimately harming their growth. However, online payments, when done right, are actually more secure than traditional offline payments, as they provide the ability to identify fraud and ensure identity authentication in card-not-present transactions.
African merchants would do well to integrate online payment solutions via PCI DSS Level 1 certified payment service providers, such as Direct Pay Online. We provide risk management algorithms and updated black list protection, further increasing the security for ecommerce users and merchants, alike.